The first step to removing unecessary delay(); from Arduino programs is to make a project with an LED that can blink without a delay(); function. That example can be extended to add a button that works to debounce without delay();
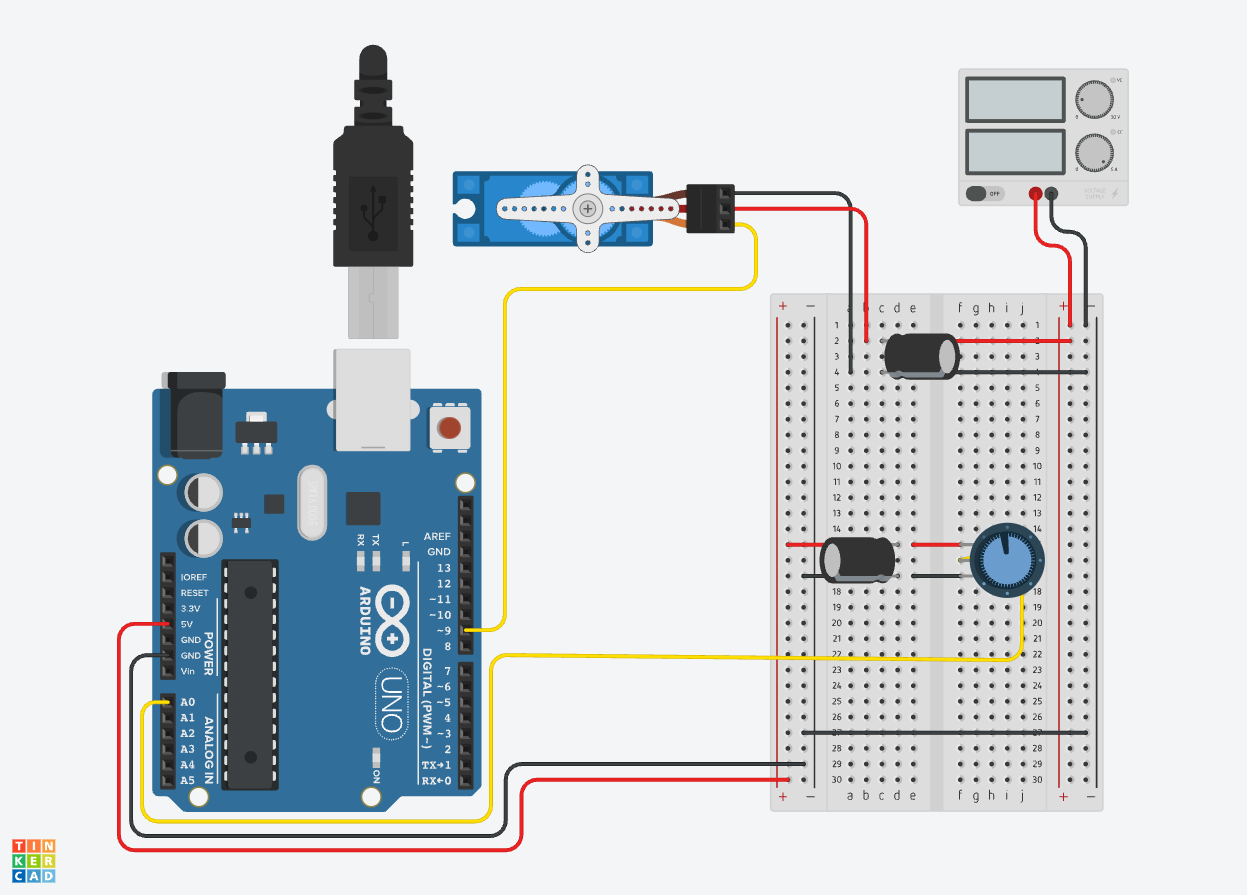
The servo examples from the Arduino documentation, sweep and knob, both use delay();. This section shows how to remove the delay from the knob example but could be applied to sweep as well by following the principles of how to remove delay(); from an Arduino sketch instructions.
Wrap the Task in a Millisecond Timer
This sketch simply takes the servo knob example from Arduino and wraps it inside the millisecond timer function from blink without delay. 1 For simple functions and timers this will work to replace delay for most sketches.
Now that the micro controller is not blocked by the delay(); other separate tasks such as playing a sound, reading a sensor (like a button), flashing an LED can happen on their own timers.
Servo Knob Without Delay Circuit
Servo Know without Delay Sketch
#include <Servo.h>
unsigned long previousMillis = 0; // will store last time servo was updated
// constants won't change:
const long interval = 15; // interval at which to update servo (milliseconds)
Servo myservo; // create servo object to control a servo
int potpin = 0; // analog pin used to connect the potentiometer
int val; // variable to read the value from the analog pin
void setup() {
myservo.attach(9); // attaches the servo on pin 9 to the servo object
}
void loop() {
unsigned long currentMillis = millis();
if (currentMillis - previousMillis >= interval) {
previousMillis = currentMillis; // save the last time you wrote to the servo
val = analogRead(potpin); // reads the value of the potentiometer (value between 0 and 1023)
val = map(val, 0, 1023, 0, 180); // scale it to use it with the servo (value between 0 and 180)
myservo.write(val); // sets the servo position according to the scaled value
}
}
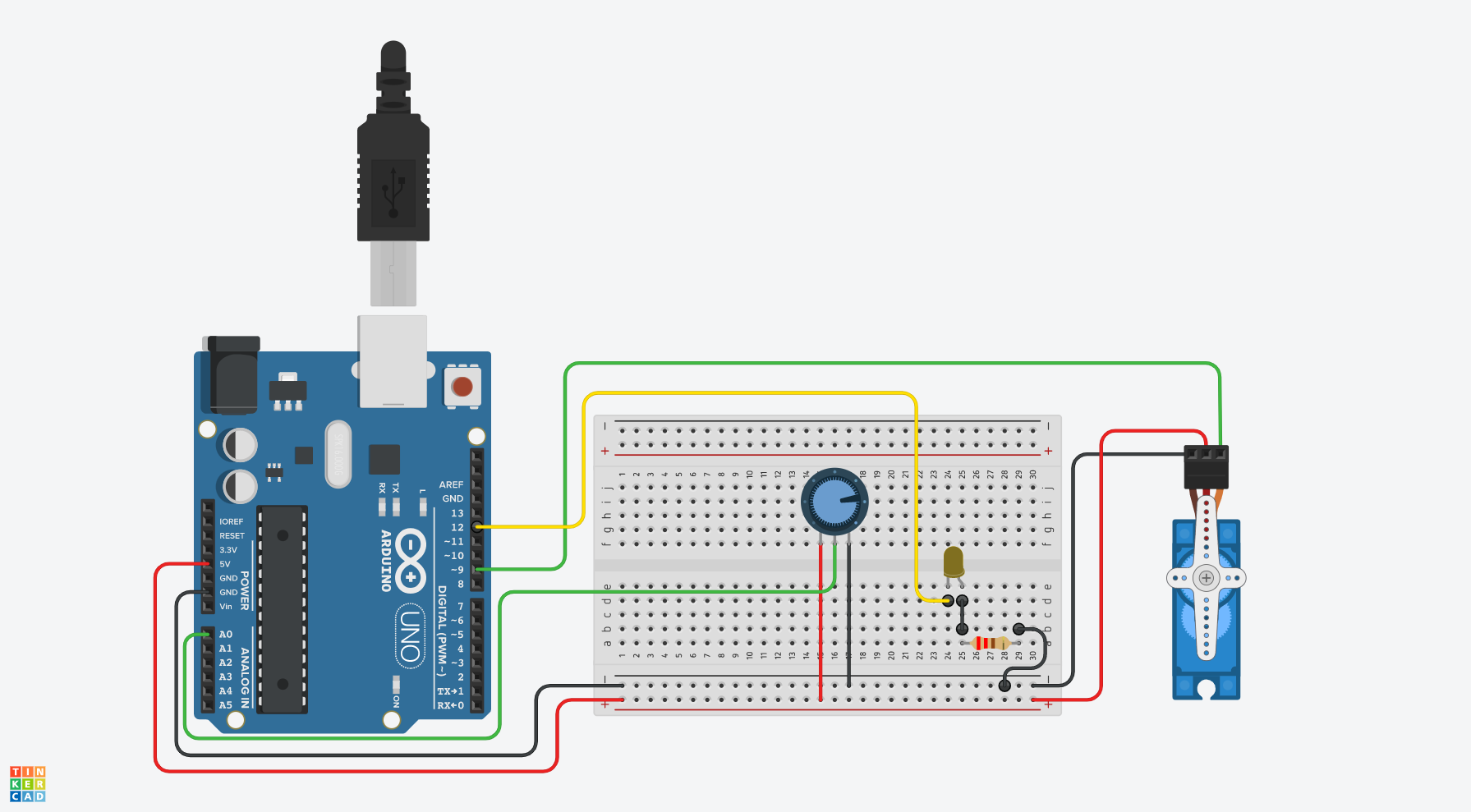
Add a Blink Without Delay LED
Example Circuit Adding a Blinking LED
Example Code With Blinking LED and Servo
#include <Servo.h>
unsigned long previousMillis = 0; // will store last time servo was updated
unsigned long LEDpreviousMillis = 0; // will store last time servo was updated
// constants won't change:
const long interval = 15; // interval at which to update servo (milliseconds)
const long LEDinterval = 1000; // interval at which to update servo (milliseconds)
const int potpin = 0; // analog pin used to connect the potentiometer
const int ledPin = 13; // Set LED Pin to 13
Servo myservo; // create servo object to control a servo
// variables will change
int val; // variable to read the value from the analog pin
int ledState = LOW; // ledState used to set the LED
void setup() {
myservo.attach(9); // attaches the servo on pin 9 to the servo object
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT); // sets LED pin as output
}
void loop() {
unsigned long currentMillis = millis(); // update to current time in milliseconds
// Servo Timer If Conditional
if (currentMillis - previousMillis >= interval) {
previousMillis = currentMillis; // save the last time you wrote to the servo
val = analogRead(potpin); // reads the value of the potentiometer (value between 0 and 1023)
val = map(val, 0, 1023, 0, 180); // scale it to use it with the servo (value between 0 and 180)
myservo.write(val); // sets the servo position according to the scaled value
}
// LED Timer If Conditional
if (currentMillis - LEDpreviousMillis >= LEDinterval) {
// save the last time you blinked the LED
LEDpreviousMillis = currentMillis;
// if the LED is off turn it on and vice-versa:
if (ledState == LOW) {
ledState = HIGH;
} else {
ledState = LOW;
}
// set the LED with the ledState of the variable:
digitalWrite(ledPin, ledState);
}
}